Blockchain technology and cryptocurrencies have grown from niche interests to become essential components of the digital economy in recent years. These technologies have enormous transformational potential that might change everything from supply chains to finance and much more. This blog post analyzes the foundations of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology, their effects on different industries, and their possibilities in the future.

Understanding Cryptocurrency
1. What is Cryptocurrency?
Cryptocurrency is a type of digital or virtual currency that uses cryptographic techniques for security. Cryptocurrencies differ from government-issued fiat currencies by being decentralized and utilizing blockchain technology.
2. Key Characteristics of Cryptocurrency
- Decentralization: Most cryptocurrencies operate on decentralized networks based on blockchain technology. This means they are not controlled by any single entity, such as a government or financial institution.
- Security: Cryptocurrencies use cryptographic methods to secure transactions and control the creation of new units. This ensures that transactions are secure and tamper-proof.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology, which underpins cryptocurrencies, provides a public ledger of all transactions. This ledger is immutable, meaning once data is recorded, it cannot be altered.
- Anonymity is maintained as transactions are logged on a public ledger, but users’ identities usually remain pseudonymous.
3. Popular Cryptocurrencies
- Bitcoin (BTC): Launched in 2009 by an anonymous entity known as Satoshi Nakamoto, Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency. It is often referred to as digital gold due to its limited supply and store of value characteristics.
- Ethereum (ETH): Proposed by Vitalik Buterin in 2013 and launched in 2015, Ethereum extends beyond just cryptocurrency. It enables the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
- Ripple (XRP) aims to streamline real-time cross-border payments, gaining recognition for its rapid transaction speeds and minimal fees.
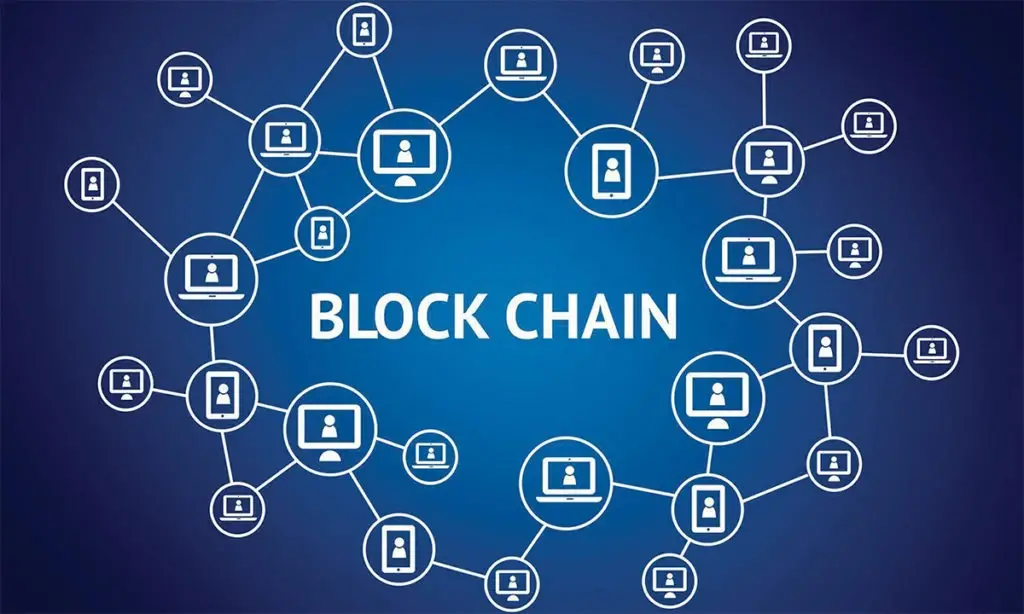
Blockchain Technology Explained
1. What is Blockchain?
A blockchain is a distributed ledger technology that maintains a secure and decentralized record of transactions across a network of computers. Each block in the chain contains a list of transactions, and each block is linked to the previous one, forming a chain.
2. How Does Blockchain Work?
- Blocks and Transactions: Each block contains a list of transactions. Once a block is filled with transactions, it is validated and added to the chain.
- Decentralization occurs as a network of nodes (computers) keeps the blockchain running, with each node holding a complete copy. For changes to be added to the chain, the majority of these nodes must validate them first.
- Consensus Mechanisms: To add new blocks, the network must agree on the validity of transactions through consensus mechanisms. Common mechanisms include Proof of Work (PoW) and Proof of Stake (PoS).
3. Types of Blockchains
- Public Blockchains: These are open to anyone and are maintained by a distributed network of nodes. Bitcoin and Ethereum are examples of public blockchains.
- Private blockchains are governed and restricted by a single organization or a specific group, frequently serving businesses for their internal needs.
- Consortium blockchains involve a group of organizations managing the system together, often used when multiple parties need to collaborate while preserving a degree of privacy.
The Impact of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
1. Financial Services
- Banking: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology offer an alternative to traditional banking systems. They enable peer-to-peer transactions without the need for intermediaries, potentially reducing costs and increasing efficiency.
- Cross-Border Payments: Cryptocurrencies facilitate faster and cheaper cross-border transactions compared to traditional methods. Ripple, for example, is designed to streamline international payments.
- DeFi (Decentralized Finance): DeFi platforms use blockchain to offer financial services like lending, borrowing, and trading without traditional intermediaries. These platforms leverage Ethereum and other blockchains that support smart contracts.
2. Supply Chain Management
- Transparency and Traceability: Blockchain technology can enhance transparency in supply chains by providing a tamper-proof record of the provenance and journey of goods. This can help in verifying the authenticity of products and ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Efficiency: Automating processes through smart contracts can streamline operations and reduce delays in supply chains. For example, a smart contract can automatically execute payment when certain conditions are met.
3. Healthcare
- Data Security: Blockchain can secure patient records and ensure they are accessible only to authorized parties. This can improve patient privacy and reduce the risk of data breaches.
- Drug Traceability: Blockchain can track the production and distribution of pharmaceuticals, helping to prevent counterfeit drugs and ensuring that only genuine products reach consumers.
4. Voting Systems
- Election Integrity: Blockchain-based voting systems can provide a transparent and tamper-proof record of votes. This could enhance trust in electoral processes and reduce the risk of fraud.
- Accessibility: Blockchain voting can offer secure and accessible voting options for people who are unable to vote in person, potentially increasing voter participation.
Challenges and Considerations
1. Scalability
- Transaction Speed and Costs: As blockchain networks grow, they can face challenges related to transaction speed and costs. For instance, Bitcoin and Ethereum have experienced congestion and high fees during periods of high demand.
- Developers are creating various scaling solutions, including layer-2 technologies like Bitcoin’s Lightning Network and new consensus mechanisms such as Ethereum 2.0’s shift to Proof of Stake.
2. Regulatory and Legal Issues
- Regulation: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain technologies face an evolving regulatory landscape. Governments and regulatory bodies are working to address issues related to security, fraud, and compliance.
- Legal Challenges: The legal status of cryptocurrencies varies by country, affecting their adoption and use. Some countries have embraced them, while others have imposed restrictions or outright bans.
3. Security Risks
- Although blockchain technology offers high security, applications built on it can still face vulnerabilities to hacking. Notable incidents include the hacks of cryptocurrency exchanges and DeFi platforms.
- Fraud and Scams: The pseudonymous nature of cryptocurrencies can make it easier for fraudulent activities to occur. Investors should be cautious of schemes promising high returns with little risk.

The Future of Cryptocurrency and Blockchain
1. Integration with Traditional Systems
- Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): Many countries are exploring or developing their own digital currencies issued by central banks. CBDCs aim to combine the benefits of cryptocurrencies with the stability and regulatory oversight of traditional fiat currencies.
- Interoperability: Future advancements may focus on improving interoperability between different blockchain networks and traditional financial systems. This could enhance the usability and integration of blockchain technology.
2. Technological Innovations
- Advanced Consensus Mechanisms: Innovations in consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Space and Proof of Authority, aim to address the limitations of existing systems and improve scalability and efficiency.
- Blockchain as a Service (BaaS): Companies are increasingly offering blockchain solutions as a service, allowing businesses to implement blockchain technology without needing to build and maintain their own infrastructure.
3. Societal Impact
- Economic Inclusion: Cryptocurrencies and blockchain have the potential to enhance financial inclusion by providing access to financial services for unbanked and underbanked populations.
- Decentralized Governance: The rise of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) presents new models for governance and decision-making, potentially transforming how organizations and communities operate.

Conclusion
Cryptocurrency and blockchain technology represent a paradigm shift in the way we think about and manage value and information. While there are still many challenges to address, the potential benefits and applications of these technologies are vast. From revolutionizing financial services and supply chains to enhancing data security and voting systems, the impact of cryptocurrency and blockchain is profound and far-reaching.
As we continue to explore and develop these technologies, it is crucial to remain informed and vigilant about their evolving landscape. Whether you are an investor, a business owner, or simply a curious observer, understanding the world of cryptocurrency and blockchain is essential for navigating the future of our digital economy.
With ongoing advancements and growing adoption, the journey of cryptocurrency and blockchain is only beginning. Seize the opportunities, keep yourself updated, and get ready for a future where these technologies will be central to shaping our world. Tech-arcis